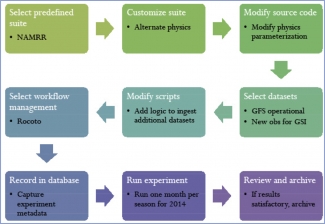
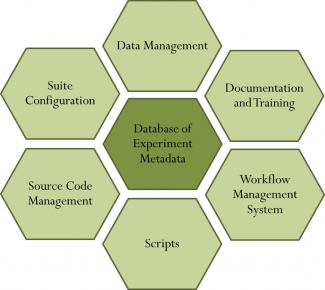
Source code management and build systems Source code repositories for all workflow components need to be available and accessible to the community. Fast, parallel build systems should be implemented to efficiently build all workflow components of a suite before experiments are conducted.
Suite definition and configuration tools All configurable aspects of a suite are abstracted to files that can be edited to create the experiments. Predefined suites are provided as a starting point for creating experiments, with scientists also having the option to compose their own suites.
Scripts The scripting is such that each workflow component (e.g., data assimilation) is associated with a single script, regardless of which suite is being run.
Workflow automation system The workflow automation system handles all job submission activity. Hence, the scripts used to run workflow components do not contain job submission commands.
Documentation and training Documentation and training on all workflow components and suites are readily available through electronic means.
In addition to the elements above, standardized tools for data visualization and forecast verification need to be available to all scientists.
Next steps for NITE: Modernization of the modeling infrastructure at NCEP is very important for community involvement with all NCEP suites, and with the Next Generation Global Prediction System (NGGPS) in particular. The recommended implementation approach for NITE includes several phases, to minimize disruption to operational systems, and limit implementation costs, while providing useful, incremental capabilities that will encourage collaboration. Ongoing discussions between EMC and DTC, especially in the context of NGGPS infrastructure modernization, will likely lead to NITE implementation in the coming years.
See http://dtcenter.org/eval/NITE